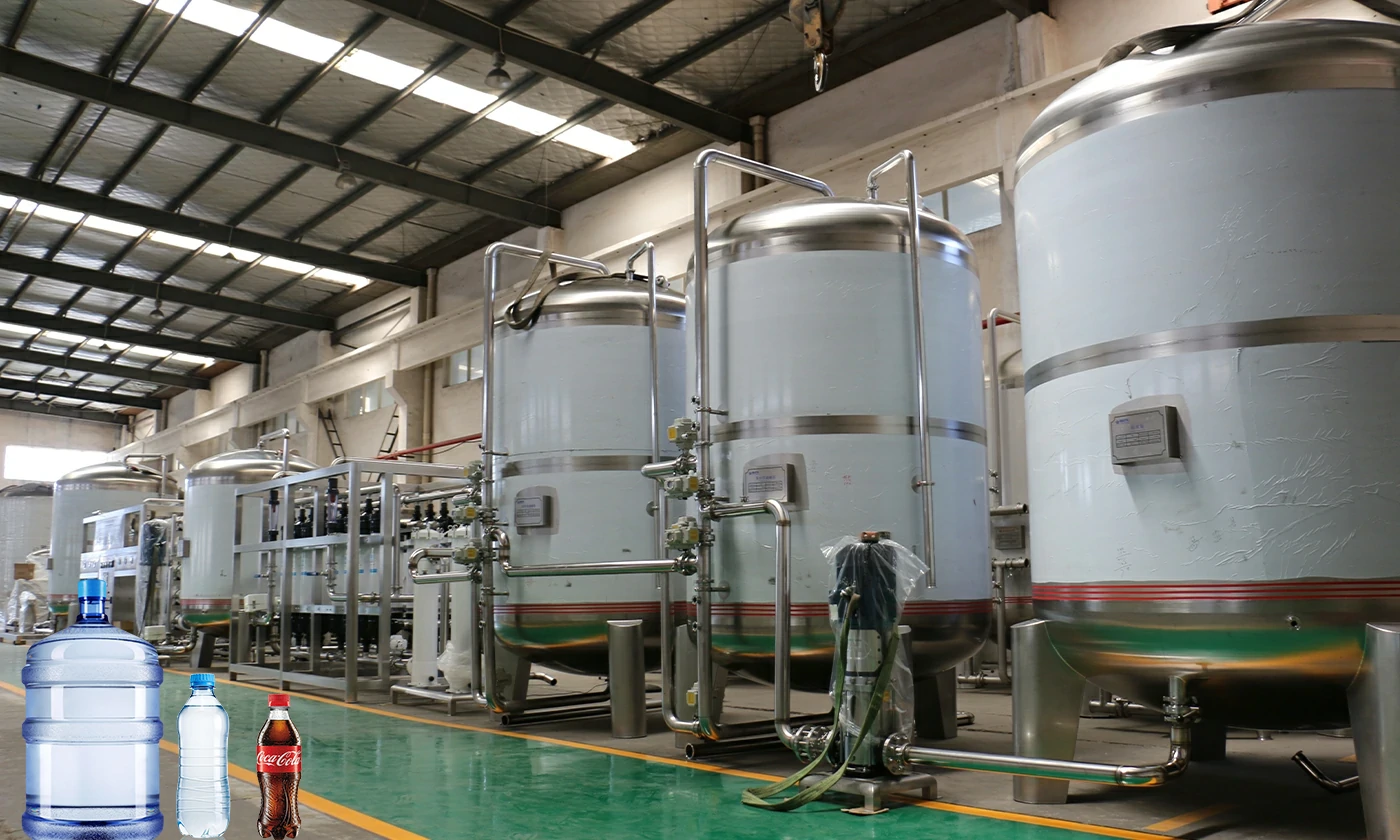
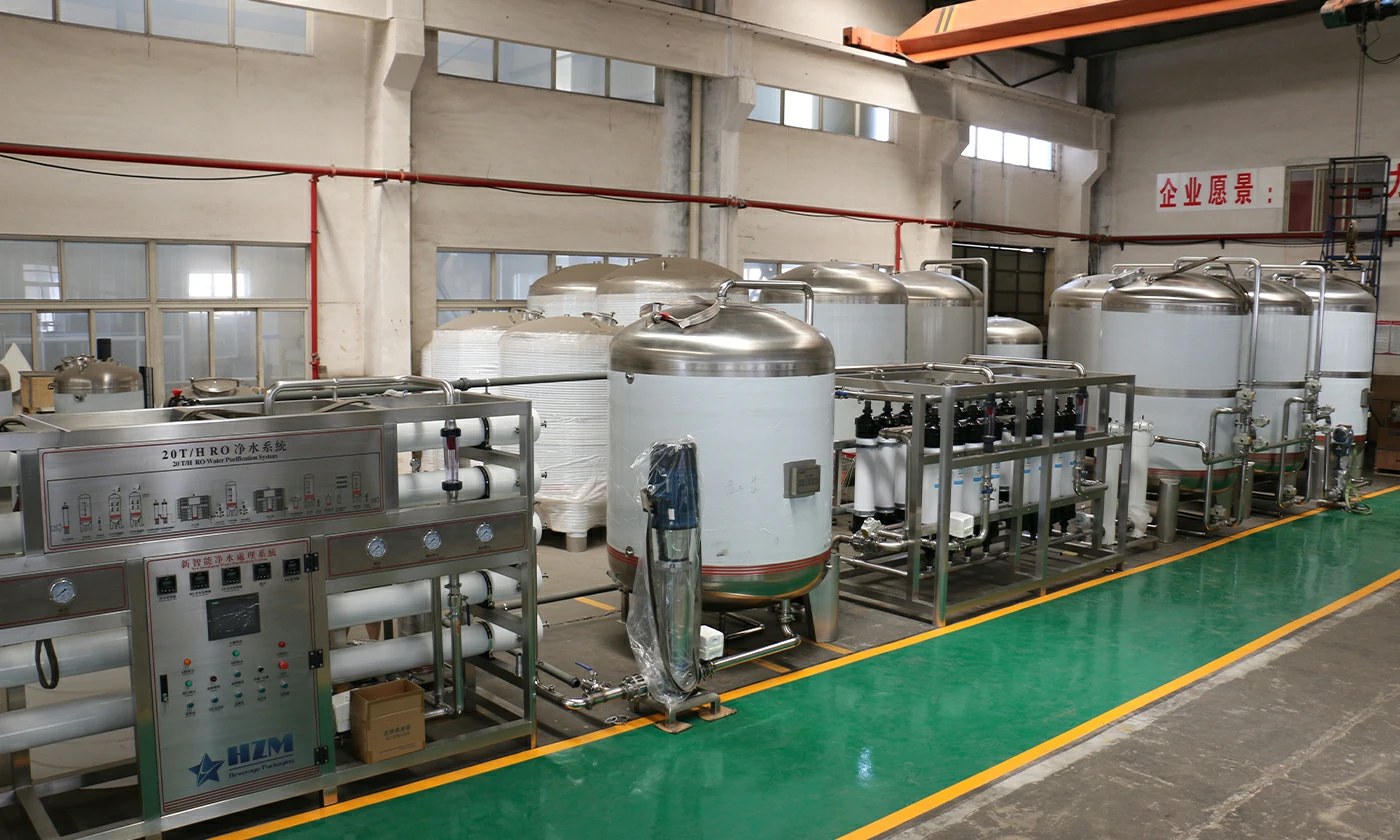
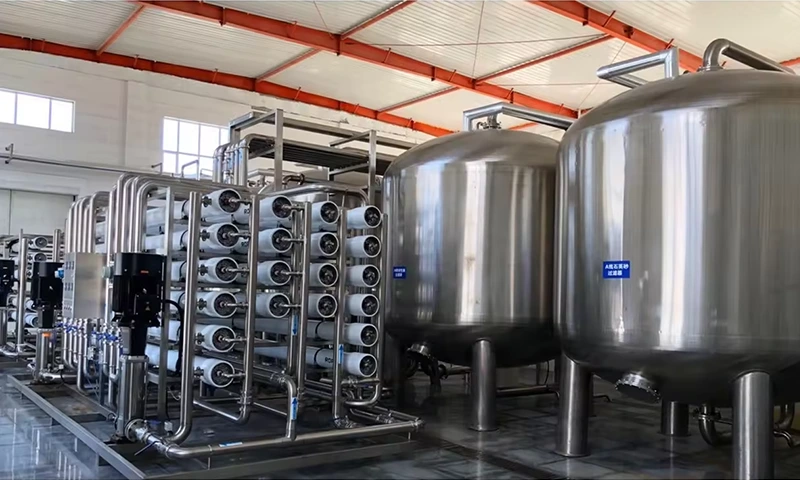
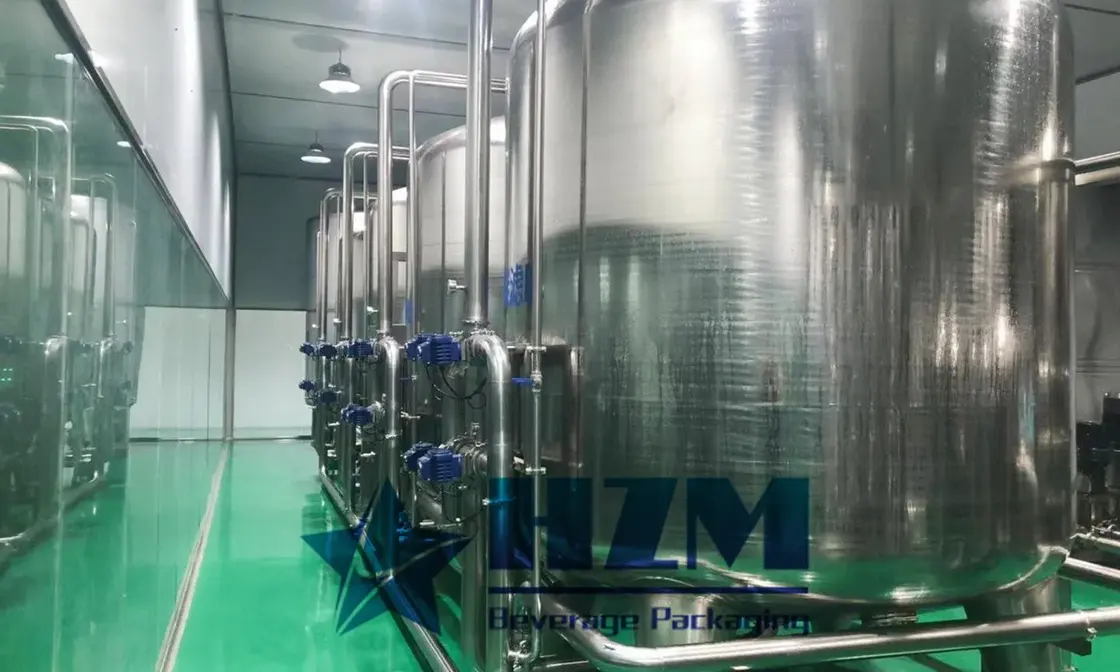
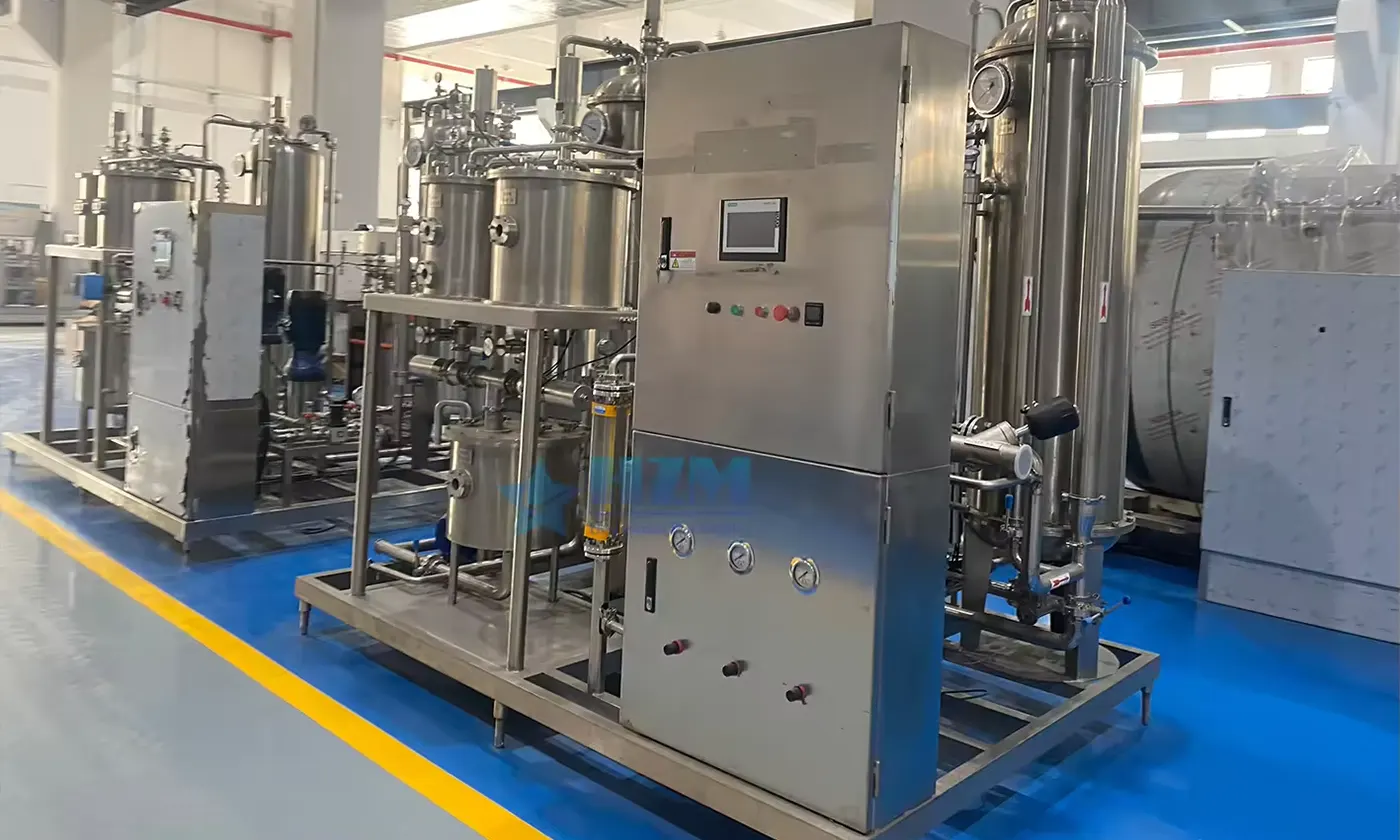
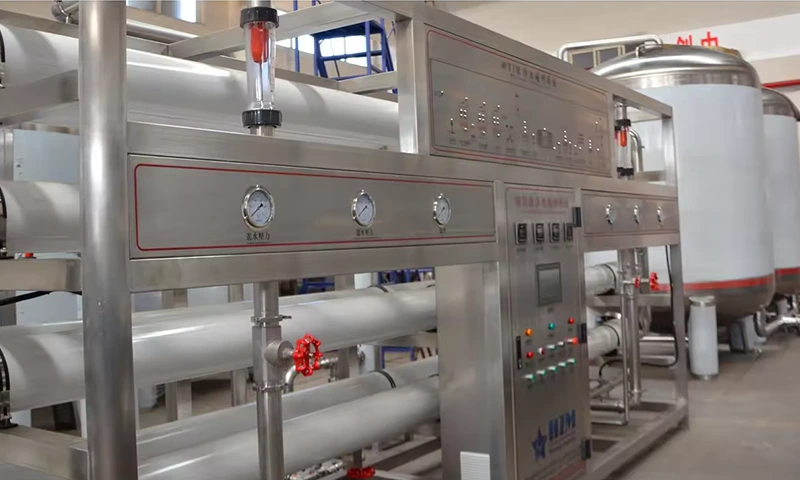
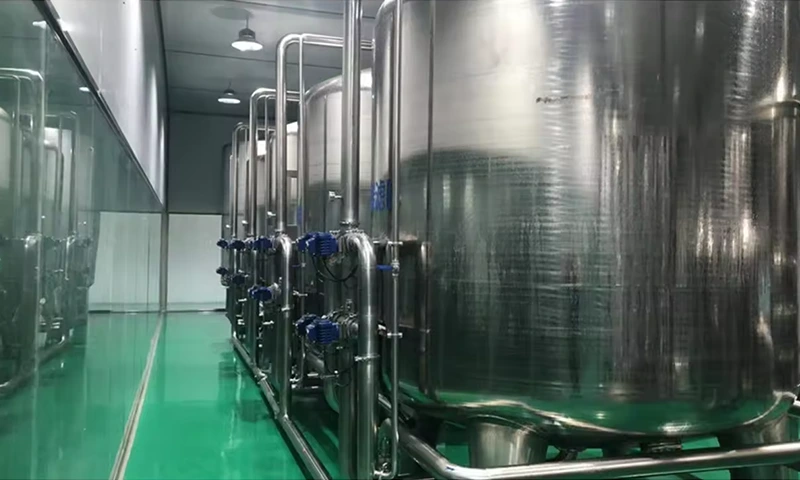
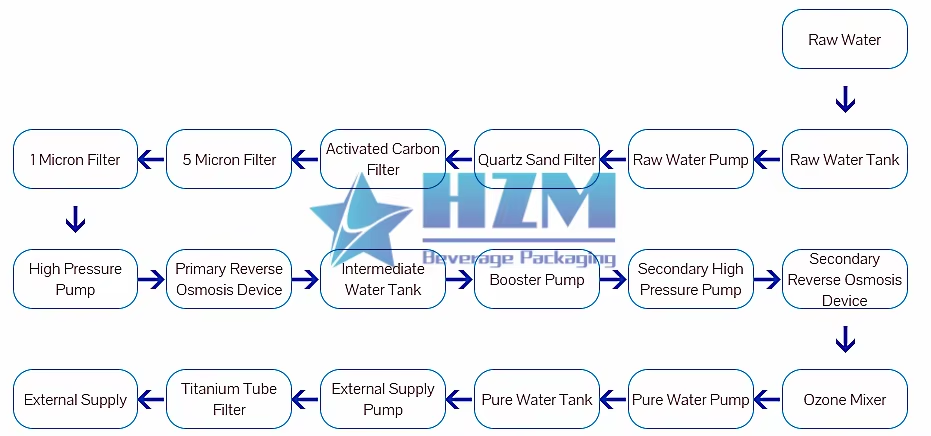
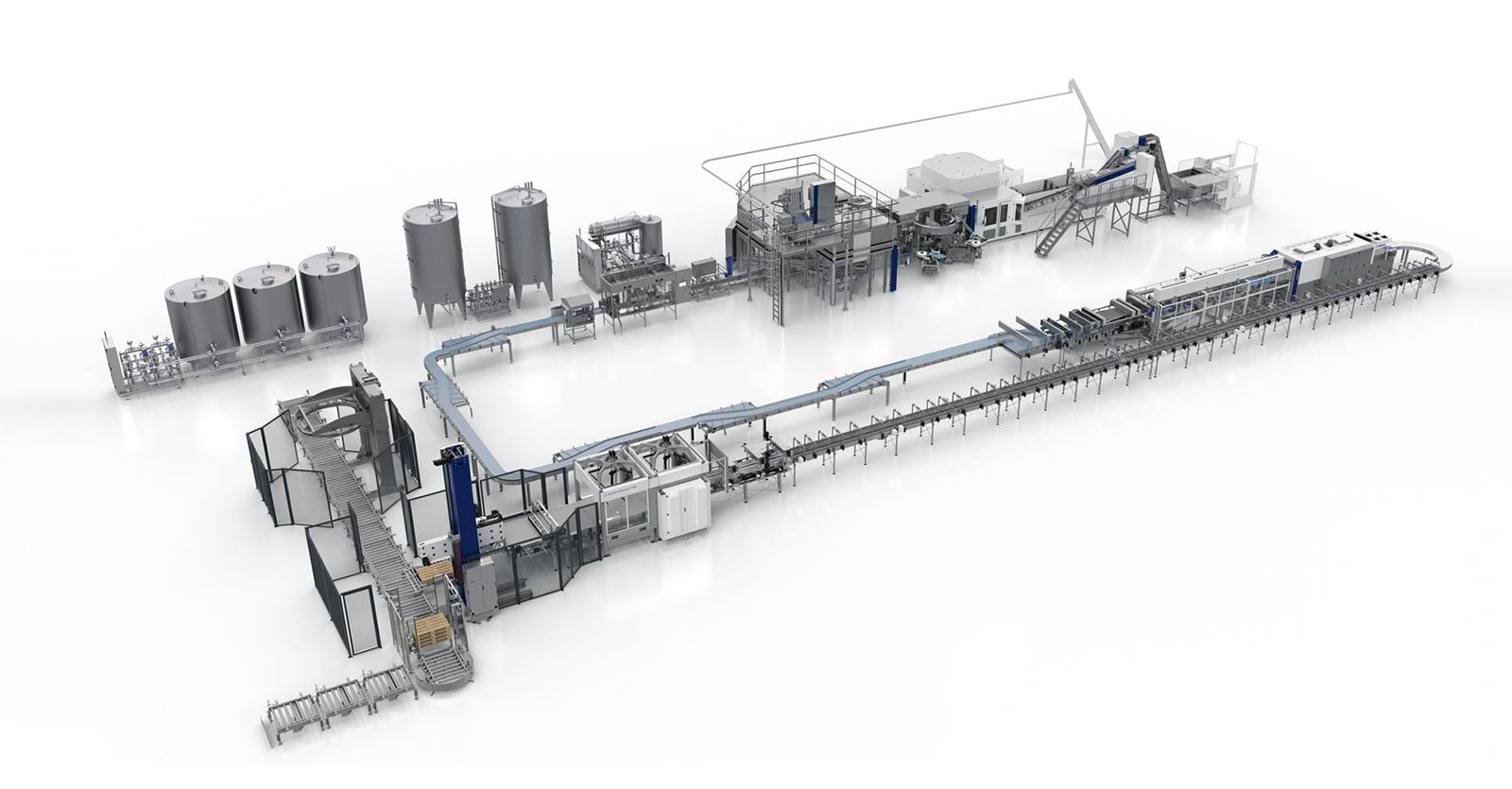
1. Sand filter Also known as "mechanical filter" or "Multi media filter" Composition: mainly composed of pressure vessel and Filter material composition. Particle size difference is laid in layers under pressure a filter bed is formed in the pressure vessel.
Function : Remove solid particles, colloids and suspended solids in the water source, reduce the pollution index SDI < 5, and ensure the safety of reverse osmosis membrane.
2.Activated carbon filter is composed the activated carbon filter is composed of pressure vessel and activated carbon filter material.

Function : Activated carbon has a porous structure and strong adsorption. It can effectively remove organic matter, colloidal substances and residual chlorine (< 0.1mg / L), reduce chromaticity, remove peculiar smell, improve the taste of water and protect the safety of RO membrane.
3. Softening device is composed of ion exchange resin (multi sodium type), pressure vessel, salt tank and regeneration cleaning control mechanism.
Function : Metal (calcium, magnesium, etc.) ions in water are replaced by ion exchange of resin.
2RNa+Ca2+=R2 Ca+2Na+
2RNa+Mg2+=R2Mg+2Na+
4. Precision filter (or security filter)it is composed of filter element (filter element with pore diameter ≤ 5 microns is recommended) and stainless steel pressure vessel.

Function : The precision filter is set to intercept the possible damage of suspended particles to the high-pressure pump and RO membrane.
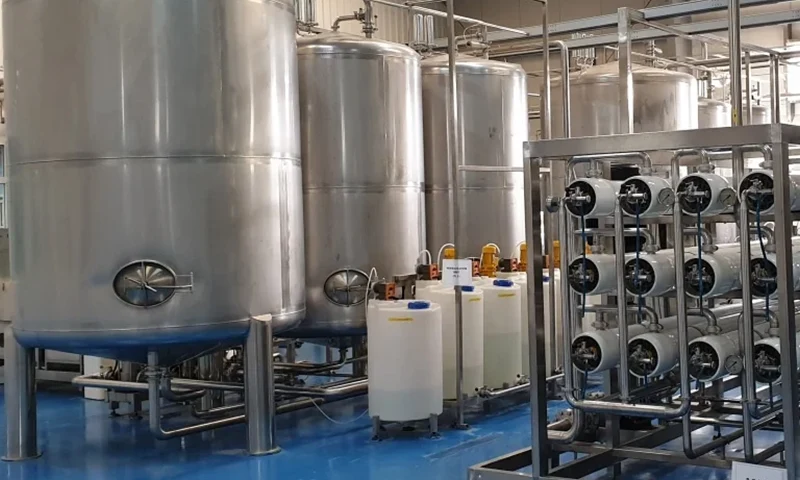
5. Flocculant: when the suspended solids content in the water source is high, adding a certain concentration of flocculant can further reduce the pollution index SDI. The mechanism is to destroy the electrical neutrality of colloid and make it flocculate and precipitate.
6. Scale inhibitor: adding an appropriate amount of scale inhibitor into the RO inlet water can inhibit the scaling of minerals on the surface of reverse osmosis membrane (concentrated water side).
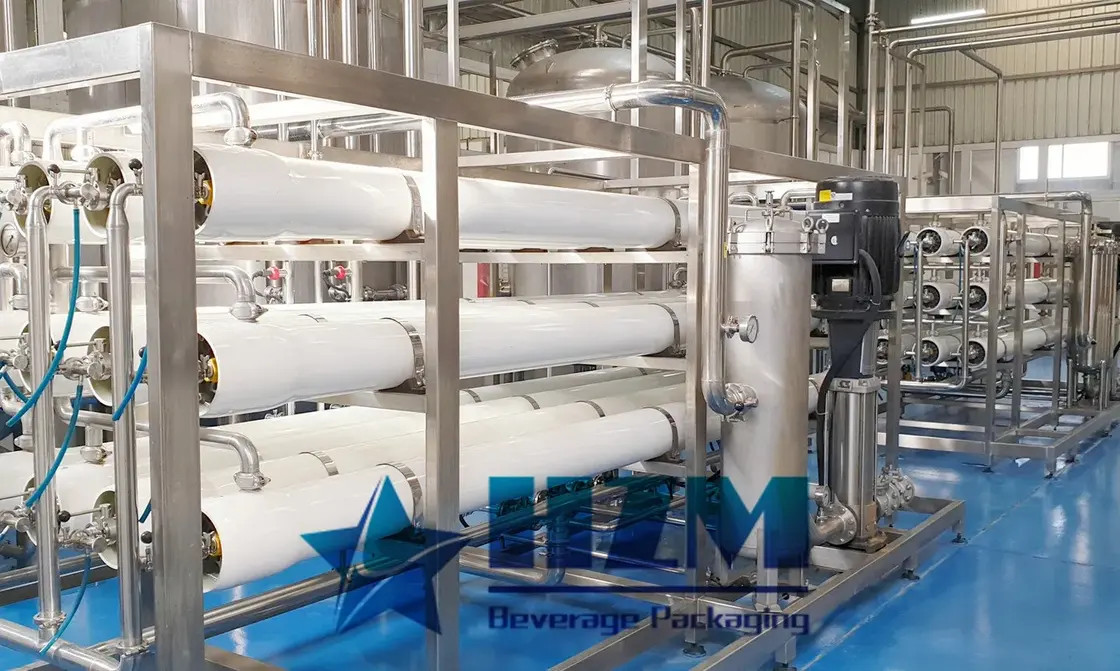
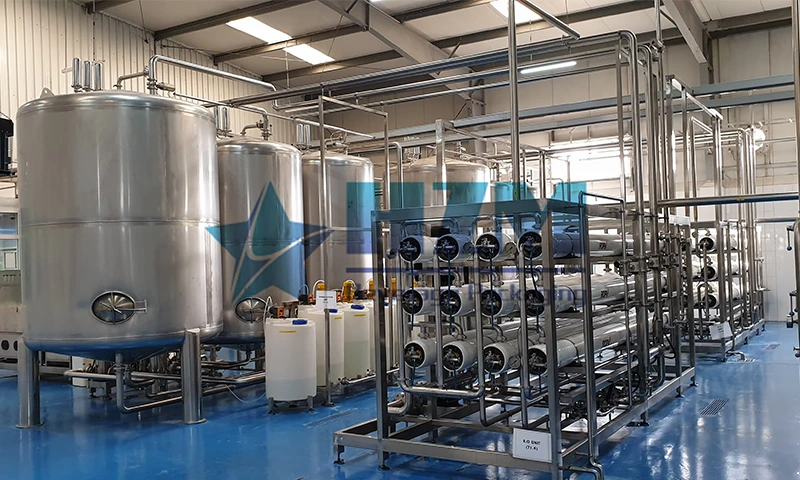
Deep treatment

Reverse osmosis is a membrane separation technology, which is a process of separating solvent and solute under pressure.
Terminal treatment
Ultraviolet disinfection: nucleoproteins in microorganisms are denatured due to the absorption of broad-spectrum ultraviolet energy, causing metabolic disorders and loss of reproductive ability. When the irradiation dose increases to a certain amount, the microbial cells are destroyed and killed.
Ozone disinfection

Ozone is a strong oxidant, and the sterilization process is a biochemical oxidation reaction.