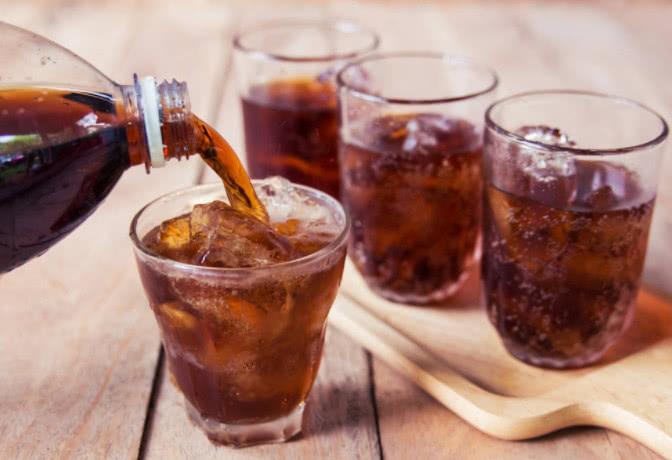
What is the role of carbon dioxide in soft drinks?
Carbon dioxide is an important component of carbonated beverages and a defining characteristic of such drinks. The role of carbon dioxide in carbonated beverages includes the following:

- Provides a cooling sensation by removing heat from the body: When people consume carbonated beverages, the carbon dioxide in the drink undergoes decomposition into carbon dioxide and water due to heating and a decrease in pressure. As the carbon dioxide escapes from the body, it takes away heat, giving a refreshing sensation. Therefore, carbonated beverages containing carbon dioxide have a cooling effect, especially during the summer, helping to relieve heat.
- Generates a distinct flavor: Carbon dioxide can interact with other ingredients in the beverage to create a unique flavor profile. As carbon dioxide escapes from the beverage, it carries away aromatic compounds, enhancing the flavor characteristics.
- Inhibits the growth and reproduction of microorganisms, extending shelf life: Carbon dioxide in the beverage alters the environmental conditions for the normal growth and reproduction of microorganisms, creating an oxygen-deficient environment that inhibits their growth. It is generally believed that a gas content of 3.5 to 4 times or more can completely inhibit microbial growth and even cause their death, thereby extending the shelf life of the beverage.
Overall, carbon dioxide plays a vital role in soft drinks by providing a cooling sensation, contributing to distinctive flavors, and acting as a natural preservative to inhibit microbial growth, thus extending the shelf life of the product.
TAG: Co2 mixer machine CO2 Saturator
-
![Core Selling Points of Glass Bottle CSD Filling & Capping Line]()
Core Selling Points of Glass Bottle CSD Filling & Capping Line
-
![Customizable beverage filling system]()
Customizable beverage filling system
-
![Differences Between Hot Filling and Cold Filling in Beverage Filling Machines]()
Differences Between Hot Filling and Cold Filling in Beverage Filling Machines
-
![Selecting a Dedicated RO Reverse Osmosis Water Treatment System for a Purified Water Beverage Production Line]()
Selecting a Dedicated RO Reverse Osmosis Water Treatment System for a Purified Water Beverage Production Line
-
![How Fast Is the Labeling Speed of Tea Beverage Packaging Machines?]()
How Fast Is the Labeling Speed of Tea Beverage Packaging Machines?