The 6 Elements of Tea Beverage Production that Affect Quality

Tea beverages are called "new era beverages" internationally. From a long-term perspective, they can compete with carbonated beverages. Their characteristics are natural, healthy, and thirst-quenching, which meets the consumption psychology needs of modern people who advocate natural, health and wellness
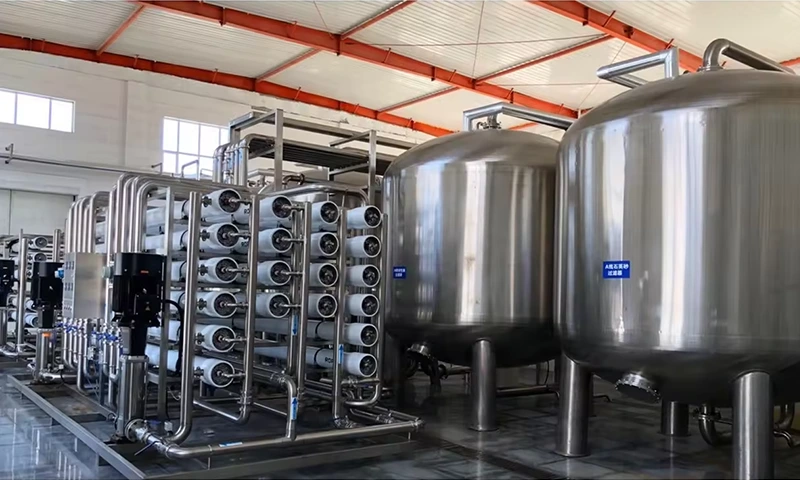
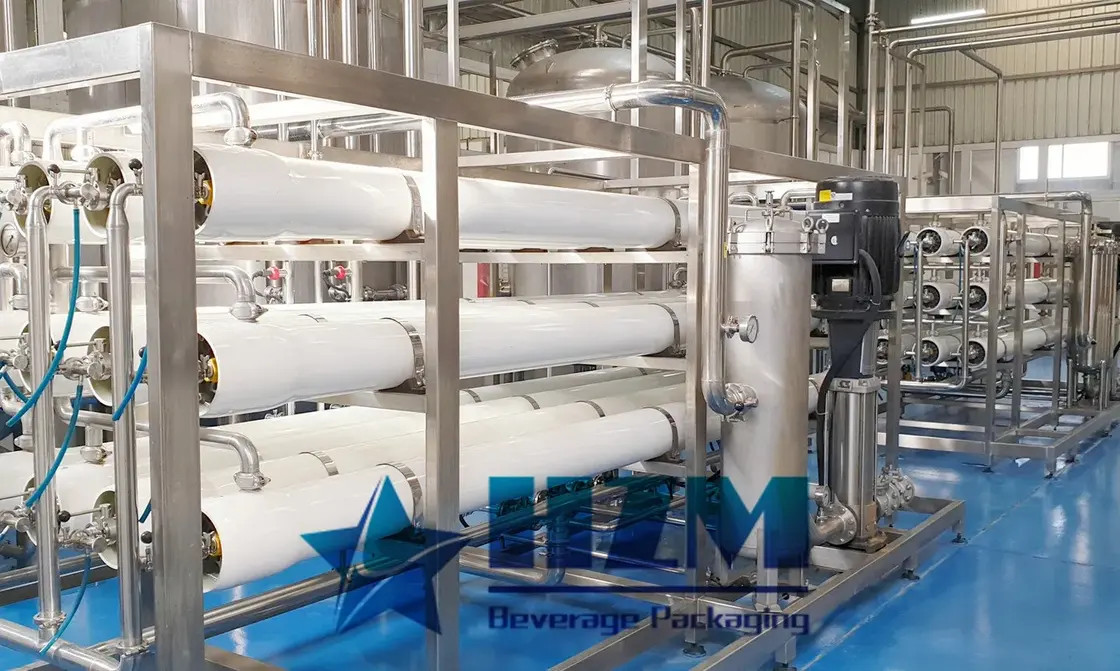
- Water quality: Water is the main component of tea beverages and has a significant impact on their quality. The ions in water such as calcium, magnesium, iron, and chlorine can affect the color and flavor of the tea, causing turbidity and the formation of tea cream. When the iron ion content in water exceeds 5ppm (5 parts per million), the tea soup will turn dark and taste bitter. A high concentration of chlorine ions will make the tea soup smell rotten. Tannins in tea leaves can react with various metal ions to generate various colors. Therefore, tap water cannot be directly used to produce tea beverages. High-quality tea beverages must use pure water that has had ions removed, with a pH value between 6.7 to 7.2, an iron ion content less than 2ppm, and a chemical substance content of permanent hardness less than 3ppm.
- Raw materials: Tea can be divided into six categories: green tea, black tea, oolong tea, black tea, white tea, and yellow tea, each with its own unique flavor. The flavor of finished tea is determined by the quality of the tea, its origin, tea processing techniques, storage conditions, and soluble components. The quality of the tea is closely related to the tea tree variety, the soil and sunshine conditions of the growing area, the fertilizers used, the cultivation methods, the picking season, and the moisture content of the tea buds. The quality of finished tea depends on the processing techniques, such as the thickness of tea leaves during fermentation, fermentation time control, baking temperature, and moisture control. Improper storage of high-quality finished tea can cause dampness or mold growth, resulting in a decrease in the quality of tea beverage products.
- Extraction: The factors that directly affect the extraction rate of soluble substances in tea and the quality of the extract are water temperature, extraction time, particle size of raw materials, tea-to-water ratio, and extraction method. The higher the water temperature, the longer the extraction time, the smaller the particle size of the raw materials, and the higher the tea-to-water ratio, the higher the extraction rate and the more bitter the tea soup will be, increasing costs, and affecting the freshness of the aroma. Whether multi-stage extraction methods are used also affects the quality of the tea soup. The key technology in the production of tea beverages is to avoid and eliminate turbidity and precipitation in the tea beverages. The white tea cream precipitate that forms after the tea extract cools is formed by the reaction between tea polyphenols and their oxidized decomposition products and caffeine-chromium. Industry experts call it "tea cream cheese". Proteins, pectin, and starch molecules are also prone to precipitation, and the ions in water are the primary cause of turbidity and precipitation.
- Tea quality: The quality of tea directly affects the taste and aroma of tea beverages. Choosing high-quality tea and conducting appropriate processing can improve the quality of tea beverages.
- Processing technology: The processing of tea beverages includes picking, withering, rolling, fermenting, and baking. Whether the processing technology is scientific and rigorous directly affects the taste and aroma of tea beverages.
- Environmental conditions: The production environment of tea beverages should have suitable temperature, humidity, and ventilation conditions to ensure the quality of tea leaves and the hygiene and safety of tea beverages. At the same time, the cleanliness and hygiene of the production environment are also one of the key factors to ensure the quality of tea beverages.
There are several methods to solve the chaos of tea beverages, and the commonly used method is the physical method - cooling the tea soup and removing it with a high-speed centrifuge or filtering it with ultrafiltration to improve the clarity of the tea soup.
TAG:



























































 Home /
Home /